26. Do a research about the inversion method to generate random variables.
Inverse transform sampling is a method for generating random numbers from any probability distribution by using its inverse cumulative distribution F−1(x). Recall that the cumulative distribution for a random variable X is FX(x)=P(X≤x). In what follows, we assume that our computer can, on demand, generate independent realizations of a random variable U uniformly distributed on [0,1]
Continuous Distributions Assume we want to generate a random variable X with cumulative distribution function (CDF) FX. The inverse transform sampling algorithm is simple:
- Generate U∼Unif(0,1)
- Let X=F−1X(U)
Then, X will follow the distribution governed by the CDF FX, which was our desired result.
Note that this algorithm works in general but is not always practical. For example, inverting FX is easy if X is an exponential random variable, but its harder if X is Normal random variable.
Discrete Distributions Now we will consider the discrete version of the inverse transform method. Assume that X is a discrete random variable such that P(X=xi)=pi. The algorithm proceeds as follows:
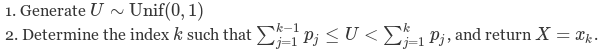
Notice that the second step requires a search. Assume our random variable X can take on any one of K values with probabilities {p1,…,pK}. We implement the algorithm below, assuming these probabilities are stored in a vector called p.vec.
