28. Do a research about the Box Muller Transform.
A Box Muller transform takes a continuous, two dimensional uniform distribution and transforms it to a normal distribution.
It is widely used in statistical sampling, and is an easy to run, elegant way to come up with a standard normal model. In fact, since it can be used to generate normally distributed random numbers, it was originally developed as a better and computationally efficient alternative to inverse sampling.
At its most basic, the Box-Muller transformations simply takes two variables that are uniformly distributed and sends them to two independent random variables with a standard normal distribution.
Let’s say U1 and U2 are our original independent random variables; they are uniformly distributed in the interval (0,1). The Box-Muller transformation creates new Z0 and Z1; independent, random variables that have a standard normal distribution:
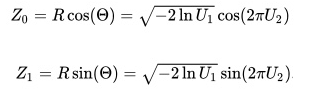
The derivation here is based on the way we can represent any point in the X,Y Cartesian plane through polar coordinates, with a radius and an angle.
